SRM. SRM. SRM.
Have you ever heard about Startup Relationship Management (SRM)?
Large companies are increasingly looking for ways to partner with startups to gain a competitive advantage and adopt the “digital native” way of working. Partnerships with tech startups make companies more agile and innovative and enable them to respond quickly to market changes.
Startups, which are an integral part of a company’s external sources of innovation, are also increasingly looking to partner with large companies for greater market access, visibility, reputation, distribution network, etc. These relationships can open other channels for important financial resources, such as corporate venture capital.
For startups:
For corporates
However, cooperation between companies and startups does not always work. On the one hand, many large established companies find it difficult to cooperate on mutually beneficial terms. On the other hand, startups often find cooperation with companies ineffective and time-consuming.
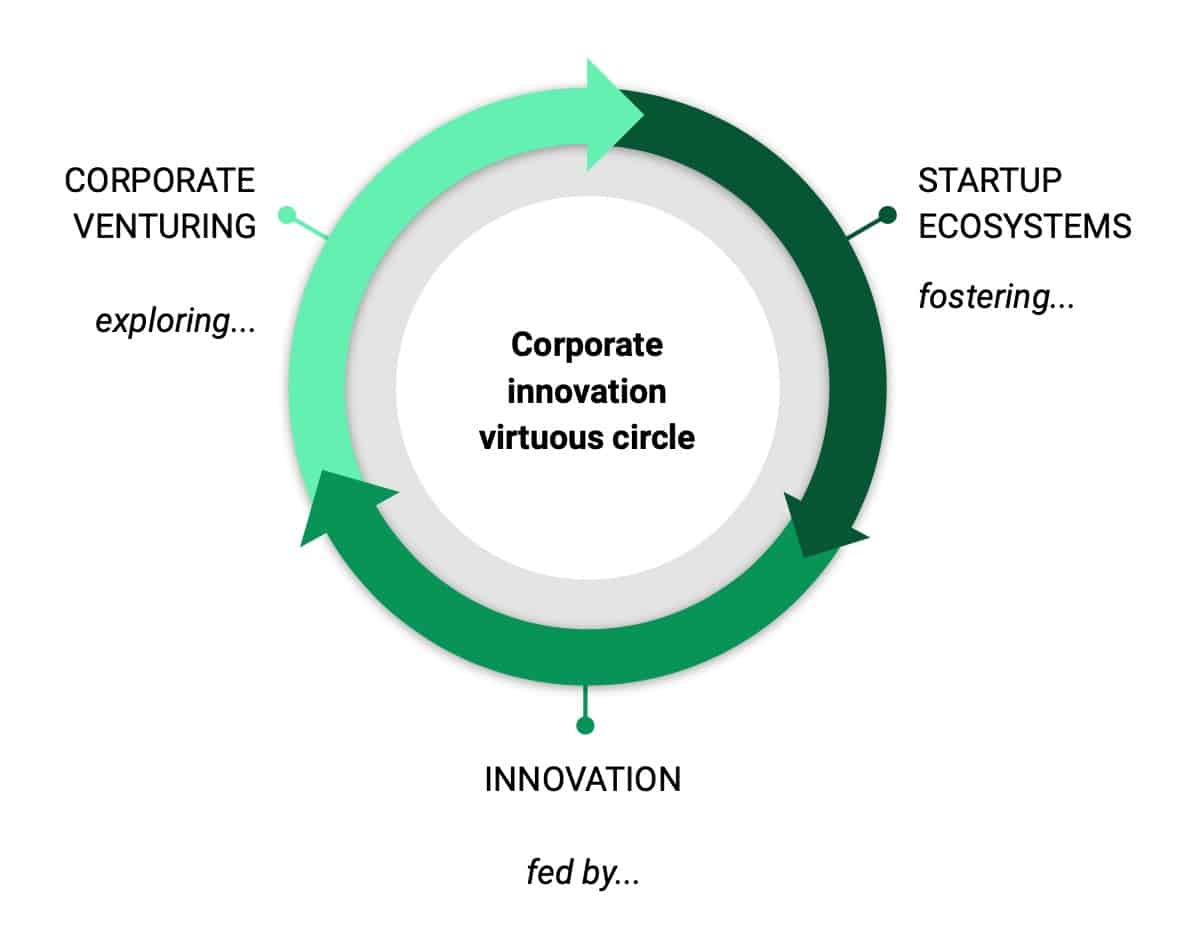
For this reason, effective Startup Relationship Management (SRM) is crucial to transform expectations into actionable plans. SRM is a method of maintaining a company’s relationship with the startup world and building a powerful and effective interface for working with newcomers. Typically, SRM in companies aims to maintain and automate startup scouting, visualise relevant startups on a startup radar and improve the quality of startup recruitment.
Startup scouting is a critical element of bringing external innovation into your organisation. In the scouting phase, companies try to find startups that could change their industry or business model, as well as startups that use new technologies to solve existing problems. Avoid resource-intensive desk-based research with appropriate automation. Collecting various data points on a single platform in a short period of time requires a lot of resources unless the system has built-in AI and intelligent data processing mechanisms.
Software-assisted scouting on a single platform and connectivity to industry-specific databases accelerate the process of finding interesting startups. This leaves more time for collaborative evaluation and selection by members of your innovation community.
Scouting insights, including new technologies and patents, emerging trends, inspirations related to a company’s business environment, are assessed and visualised using a startup radar. Take advantage of AI to identify the most promising startups with which to build future partnerships.
More and more companies are seeking flexible partnerships with startups where both sides take a risk and share in the rewards. Before investing millions in an acquisition, choosing startups wisely is important. Initial contacts with startups and ‘open doors’ are now commonplace.
For example, Bloomflow empowers innovation experts and business unit leaders to tackle their most critical challenges. Find new ideas, scout new startups, manage partner portfolios and monitor your innovation projects. From strategy, business development, innovation, R&D, and procurement to finance, with the tool you can:
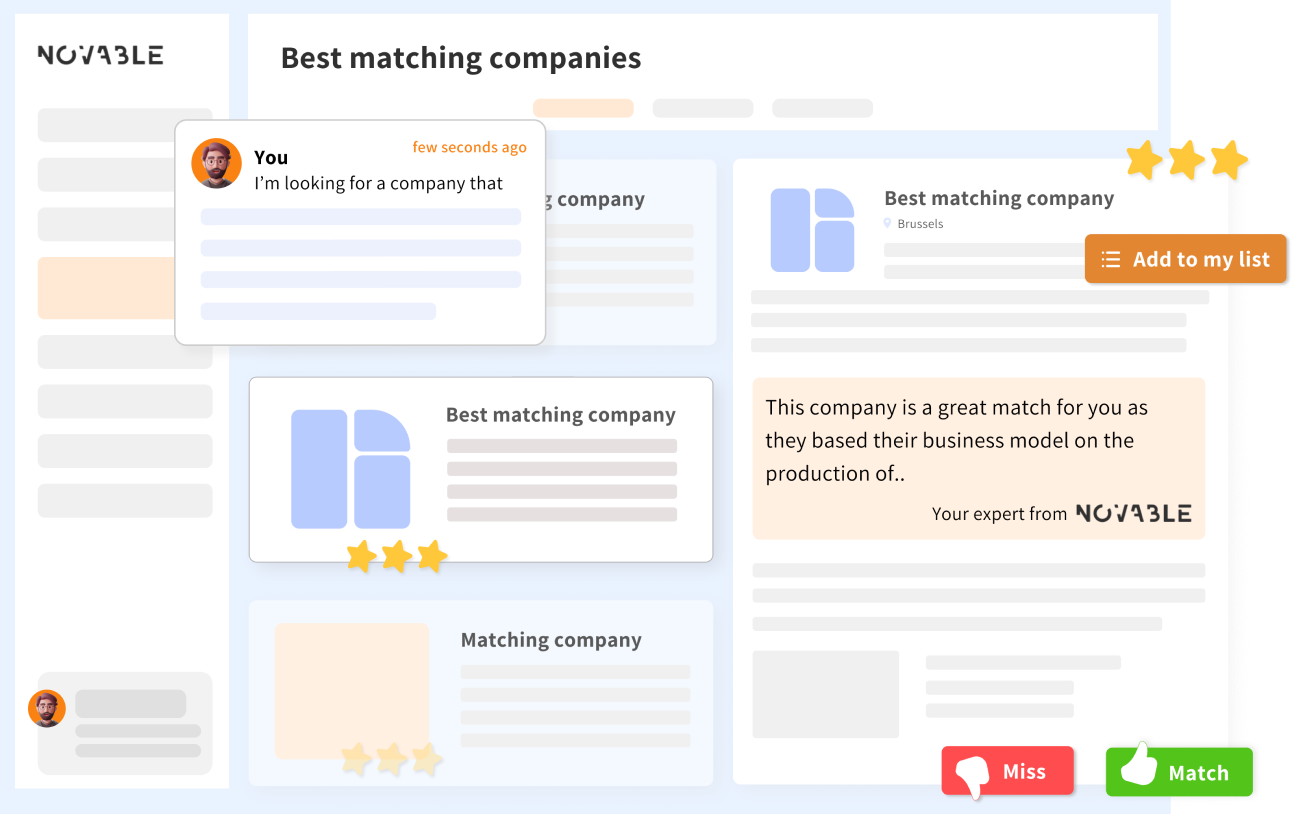
Store data such as contact information, startup funding status, geographic location, etc. Identify opportunities for collaboration and potential partnership opportunities, and make all startup data and sources accessible to all business units involved.
After deciding with whom to collaborate, companies should figure out the best strategy for working with startups. It is also time to decide how to integrate these startups into the company’s innovation framework and methodology. We distinguish five pillars from which you can choose:
Build: Startups typically serve as inspiration for larger companies to develop next-generation products and services on their own, become more agile, and leverage the latest technologies. For this reason, large companies should constantly be on the lookout for the next big thing.
Buy: Companies that are capable of developing a particular product or service internally, but lack the expertise, may acquire or invest directly to hire an external team of experts. This usually does not mean acquiring a startup, but rather specific services or capabilities offered by the startup.
Partners: More and more companies are running startup initiatives. Companies such as Daimler, DZ Bank, and Adidas consistently monitor the startup environment. The selected startups then present their projects, hold hackathons, or collaborate to overcome common challenges.
Investing: Companies invest in promising startups that are working on the latest technologies that could benefit their industry or their own growth.
Co-develop: Companies want to co-develop products with startups, leveraging their expertise in a particular area, be it a technology, methodology, or business model. In return, the startup gets access to market insights, mentoring, and business networks.
SRM will radically change the way companies and startups collaborate by creating a win-win situation where both parties are equally invested in the success of the other. Moreover, for many innovators, SRM is an indispensable part of the entrepreneurial innovation toolkit.
If you would like to learn more about the Startup Scouting process and how to build a sustainable Startup Relationship Management, feel free to contact us!
What is your opinion on the topic? Let us know what you think on LinkedIn!