Why and how are innovation scouting analysts slowly killing themselves on repetitive tasks and what can be done about it?
For a corporate venturing professional (in M&A, corporate development/CVC, or a head of innovation), most of the effort goes into disqualifying bad startup candidates. As with VCs, less than 1% of applicants (or potential matches) will end up with an engagement option.
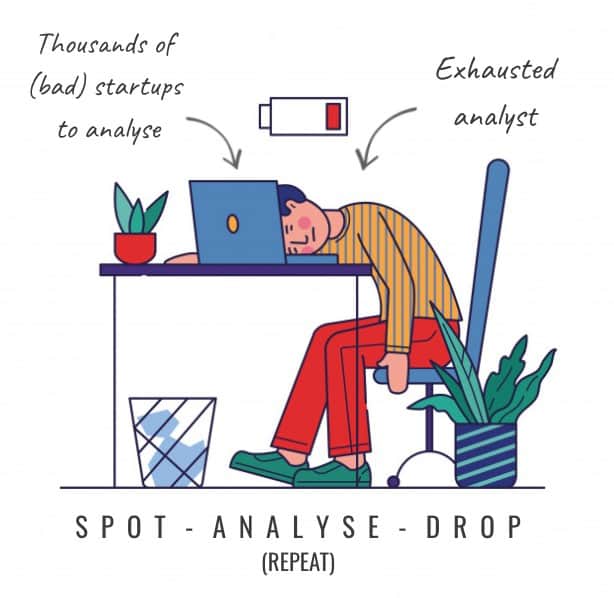
We call it the SAD syndrome, standing for: Spot — Analyse — Drop. Thousands of hours wasted in vain, with minimal progress made. Spot, analyse, drop, repeat. SAD
Although SAD poses quite an obstacle, it can be overcome. Thanks to the newly developed AI tools, they are the ones who can take on the tedious work. AI is able to read, understand, score — and match. Our estimation is that the smart use of the latest technologies can reduce analysis time by 80%, and reduce the closing time by half.
Why and how are innovation scouting analysts slowly killing themselves on repetitive tasks and what can be done about it? For a corporate venturing professional (in M&A, corporate development/CVC, or a head of innovation), most of the effort goes into disqualifying bad startup candidates. As with VCs, less than 1% of applicants (or potential matches) will end up with an engagement option. We call it the SAD syndrome, standing for: Spot — Analyse — Drop. Thousands of hours wasted in vain, with minimal progress made. Spot, analyse, drop, repeat. Although SAD poses quite an obstacle, it can be overcome. Thanks to the newly developed AI tools, they are the ones who can take on the tedious work. AI can read, understand, score — and match. We estimate that the smart use of the latest technologies can reduce analysis time by 80%, and reduce the closing time by half.